Oi & Follicle Monitoring
Ovulation Induction & Follicular Monitoring Treatment in Delhi
Ovulation Induction (OI) is a common fertility treatment used to stimulate the ovaries to produce and release eggs.
The process involves the following steps:
Initial evaluation:
The first step is a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination and some diagnostic tests, if applicable. This helps identify any underlying causes of infertility and determines the most appropriate treatment plan.
Baseline hormonal assessment:
Before starting ovulation induction, hormonal levels such as Anti Mullerian Hormone (AMH) and estradiol are measured to establish a baseline. In addition, semen analysis and tubal testing are also advised.
Ovarian stimulation:
Ovarian stimulation involves taking medication to promote the development of multiple follicles within the ovaries, each containing an egg. This is achieved by using oral medications (such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole) or injectable gonadotropins (such as follicle-stimulating hormone or human menopausal gonadotropin).
The specific medication and dosage depends on individual factors as well as the treatment plan recommended by the fertility specialist.
Follicle Monitoring:
During ovulation induction, regular monitoring is necessary to assess follicle development, hormone levels, and endometrial thickness. This process usually involves transvaginal ultrasounds and hormone blood tests. The frequency of monitoring visits will vary depending on the patient’s response to the medication.
In follicle monitoring, we check the total number of follicles, the rate at which they are growing and the endometrial thickness. We also look for structures like cyst formation, hydrosalpinges, fluid in the endometrium formation and polyp. We follow the lead follicles till they reach 17 to 20 mm in size.
The trigger injection is then given and then IUI is done 42 hours later. Otherwise, the couple is advised to try naturally. Many studies have shown that follicle rupture is strongly associated with ovulation, however other studies have also indicated that ovulation may happen even without evident follicular collapse.
This can be attributed to the fact that the oocyte can eject out of the follicle and be accepted by fimbria of the fallopian tubes, thereby going inside the fallopian tubes for fertilisation and the subsequent implantation of the fertilised eggs.
IUI is best done about 40 to 42 hours after the HCG injection. Along with this, the sperm production should be adequate. This implies more than 10 million active motile sperm per ml and the absence of any other factors such as large fibroids, polyps and hydrosalpinges.
Luteal phase support:
After ovulation, luteal phase support may be provided to help optimise the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy. This support can involve progesterone supplementation or other medications.
Pregnancy testing:
Approximately two weeks after ovulation, a pregnancy test is performed to determine if the treatment was successful.
It’s worth noting that the exact steps and medication involved in ovulation induction may vary depending on individual circumstances and the recommendations of the fertility specialist. Close monitoring and guidance from a qualified healthcare professional throughout the process are crucial to ensure high chances of pregnancy.
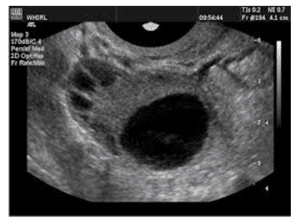
Follicular Monitoring Scan
Follicular monitoring is a crucial medical procedure utilised in the field of reproductive medicine. This process involves the regular monitoring and assessment of a woman’s ovarian follicles throughout her menstrual cycle to recommend the best fertility treatments or assess reproductive health.
During this procedure, a transvaginal ultrasound is usually used to track the growth and development of ovarian follicles. These fluid-filled sacs within the ovaries house eggs and are crucial for the reproductive process. By monitoring the size and number of these follicles, healthcare professionals can determine the best timing for IVF or IUI.
Follicular monitoring scans typically begin early in a woman’s menstrual cycle and continue until the dominant follicle(s) reach the desired size for ovulation. The aim is to gauge the precise moment when ovulation takes place, thereby deducing the ideal time for conception.
For those experiencing infertility issues, follicular monitoring is an extremely helpful means to get an insight into the functioning of their ovaries and assisting in the development of a customised treatment plan.
This non-invasive and low-risk procedure offers a thorough understanding of a woman’s reproductive cycle and can significantly increase the chances of successful pregnancy, making it a fundamental component of assisted reproductive technology. Whether seeking fertility assistance or assessing reproductive health, these scans play a huge role in helping individuals achieve their family planning goals.
Follicle Monitoring involves the tracking and assessment of ovarian follicles during the menstrual cycle, a crucial aspect of Ovulation Induction (OI). By keeping an eye on the follicles’ growth and development, our specialists can best time interventions like insemination or assisted reproductive technologies.
Follicle Monitoring during Ovulation Induction involves ultrasound examinations to visualise and measure ovarian follicles. This makes it possible for our professionals to schedule interventions precisely, optimizing the likelihood of a successful ovulation and conception.
Follicle monitoring, which gives real-time information on follicular development, is crucial for couples undergoing ovulation induction. This makes it possible to modify treatment plans in a timely manner, increasing the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
Yes, Follicle Monitoring can help identify potential issues or complications during Ovulation Induction. It allows for the early detection of irregularities, enabling prompt adjustments to the treatment plan for better outcomes.
The size and number of follicles in Follicle Monitoring for Ovulation Induction are crucial indicators of ovarian health and responsiveness to treatment. In order to increase the likelihood of a successful conception, these variables influence when the ovulation trigger or insemination occurs.