Need Help?
We are here to help.
We care for each one who come to us with hope in their hearts.

Ovarian stimulationis an important factor forthe success ofin vitrofertilization(IVF). There aretwomechanisms involved incontrolled ovarian stimulation (COH) − gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist and antagonist protocol. GnRH agonists initially produce a stimulation of the gonadotrophs resulting in secretion of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) and the expected gonadal response. Although continuous administration initially has the same effect, it is subsequently followed by down-regulation and inhibition of the pituitary–gonadal axis by clustering and internalization of the specific receptors. GnRH antagonists promptly suppress pituitary gonadotropin by competitive GnRH-receptor binding, thereby avoiding the initialstimulatory phase of the agonists and induce a rapid decrease in FSH and LH levels, preventing and interrupting premature LH surges and do not require desensitization period, so can be used in late follicular phase.[1] GnRH antagonist protocol produced a comparable ovarian response, embryo development, and pregnancy rates to GnRH agonist regime requiring lesser amounts of gonadotropins. Moreover, GnRH antagonist protocol required a shorter stimulation period plus fewer side-effects.[2] In India, the agonist protocol is time tested and still very popular. The infertility specialists are more familiar with agonist protocol and the batching is easier with this protocol. The antagonist protocol is just gaining popularity and in our center, we are using the antagonist protocol in 90% cases. The aim of the present study was to assess the clinical outcomes using GnRH antagonists in self-cycles in a private center in Delhi, India.
A retrospective analysis was made of all GnRH antagonist cycles undergoing self-IVF-embryo transfer (IVF-ET) cycles. Between July 2014 and December 2015, 510 patients underwent ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol.
Ovarian stimulation was started on day 2 with gonadotropins, recombinant human FSH (rhFSH, Folisuge; Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India or Gonal F; Merck Serono S.p.A, Italy), or highly purified menotrophin human menopausal gonadotropin (hpHMG, Menopur; Ferring GmbH, Germany) in the dose of 225–450 IU, depending on the patient’s profile [age, body mass index (BMI), previous dose of gonadotropins] till day 6 of period followed by transvaginal follicular monitoring and the dose was adjusted according to ovarian response. When follicles reached 13–14 mm, daily subcutaneous injection of GnRH antagonist, 0.25 mg Cetrorelix (Cetrotide, Merck Serono S.p.A, Italy) was added. When follicles reached 18 mm, 500 μg recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) (rhCG, Ovitrelle; Merck Serono S. p.A, Italy) was given to trigger ovulation.
Transvaginal oocyte aspiration was performed before 36 h, under ultrasound guidance, using Wallace OPU needle and Cooks gamete buffer media. Embryos were further cultured in Cooks fertilization/cleavage/ blastocyst media.
ET was done on day 2/3/5, according to the embryo growth under transabdominal USG guidance (with full bladder). After gentle insertion of speculum and suction of cervical mucus, soft outer sheath was inserted till the level of internal os. It was followed by insertion of the soft Cooks Guardia Access echotip ET catheter containing embryos in 10 μl media and 5 μl air bubble on both sides of the media and then embryos were placed in mid-uterine cavity.
Luteal support was added in the form of vaginal and injectable progesterone. Beta-hCG was done after 14 days of ET.
The measured outcomes included days of stimulation (DOS), total dose used, number of oocytes retrieved, number of embryo transferred, pregnancy, and clinical pregnancy rates. Pregnancy rates were defined as the number of positive beta-hCG cases (beta-hCG was done after 2 weeks of ET) and clinical pregnancies were defined as the presence of a fetal heart beat on ultrasonographic examination.
The demographic profile for the patients is summarized in Table 1. The mean age was 31.6 (range 24–40) years. All patients had normal cycle day 2 serum FSH levels (5–8 mIU/ml) and serum estradiol levels (35–50 pg/ml). Among all 510 subjects recruited, 313 (61.4%) presented with primary infertility and the rest 197 women (38.6%) were associated with secondary
infertility. The mean duration of infertility was 6.3 years, ranging from 2 to 18 years.
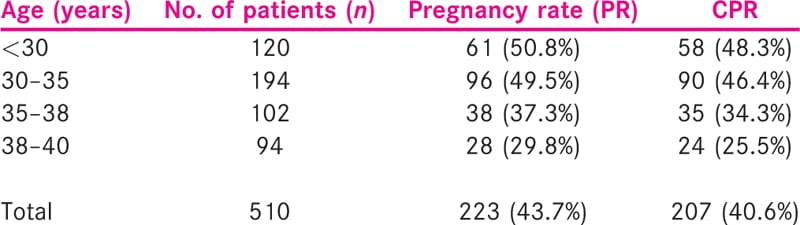
According to age group, higher pregnancy rates were seen in age <35 years [Table 2]. The average numbers of DOS were 10.3 ranging from 10 to 12 days and the total doses used were between 2400 IU and 4500 IU. The mean number of oocytes retrieved was 13.6 ranging from 11 to 16. All ETs were done on day 2/3/5 and average number of embryos transferred was 2.9 [Table 3]. There was no cancelation of cycle due to poor response. No ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) case had been noted during the study period. The total pregnancy rate was 43.7% (223/510) and out of 223 pregnancies, 16 were biochemical pregnancies. Thus, the clinical pregnancy rate was 40.6%.


The present study evaluated the effectiveness of GnRH antagonist in IVF cycles. The aim of using GnRH antagonists in IVF is the inhibition of a premature LH rise which could lead to premature luteinization, follicle maturation arrest, and asynchrony of oocyte maturation. The use of GnRH antagonists in IVF is characterized by many advantages:[3]
In India, most of the IVF specialists are using long protocol with agonist and are still doing batching. GnRH antagonist protocol produced a comparable ovarian response, embryo development, and pregnancy rates to GnRH agonist regime requiring lesser amounts of gonadotropins. Lainas et al.[4] compared the flexible GnRH antagonist and the GnRH agonist long protocols in 220 polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients undergoing IVF treatment, and found that the flexible GnRH antagonist protocol was associated with a similar ongoing pregnancy rate (50.9 versus 47.3%), lower incidence of OHSS grade II, lower gonadotropin requirement, and shorter duration of stimulation, compared with GnRH agonist. Devroey et al.[5] performed meta-analyses of various studies and stated that the treatment with antagonistswas associatedwith similar live birth rates but reduced treatment burden (duration and side effects) and less risk of ovarian stimulation syndrome, compared with GnRH agonist long protocols. In an update of a Cochrane review, 45 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) (n=7511) comparing the antagonisttothe long agonist protocolswere included and concluded that the use of antagonist compared with long GnRH agonist protocols was associated with a large reduction in OHSS [29 RCTs; odds ratio (OR) 0.43, 95% confidence interval(CI) 0.33–0.57] andthere was no evidence of a difference in live-birth rate (9 RCTs; OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.69–1.08) or ongoing pregnancy (28 RCTs; OR 0.87, 95% CI 0.77–1.00).[6] In poor responders also, GnRH antagonist had effective role. Kimet al.[7] investigatedthe effectiveness of GnRH antagonist multiple-dose protocol (MDP) with oral contraceptive pill (OCP) pretreatment in 120 poor responders undergoing IVF/ICSI, compared with GnRH antagonist MDP without OCP pretreatment and GnRH agonist low-dose long protocol (LP) and concluded that GnRH antagonist MDP with OCP pretreatment was at least as effective as GnRH agonist low-dose LP in poor responders and can benefit the poor responders by reducing the amount and duration of FSH required for follicular maturation.
GnRH antagonists in ovarian stimulation for IVF is a very friendly protocol, requiring smaller dose of gonadotropins and shorter stimulation period, requiring only 2–3 times of follicular monitoring in experienced hands with good pregnancy rate.
Nil
here are no conflicts of interest.
We care for each one who come to us with hope in their hearts.

Disclaimer – Dr Kaberi is not associated with any Hosptial/Clinic other than “Advanced Fertility and Gyne Center (AFGC)”. AFGC has only four centers at present 1. “Lajpat Nagar” 2. “CR Park Delhi” 3. “Noida” 4. “Gurgaon“.