Semen Analysis

Men contribute 50% to the causes due to problems with the sperm. The most common test is the Semen Analysis which is used to determine whether a man has an infertility problem by measuring the number and quality of sperms.
Male fertility is determined by a number of tests of which the most important is the semen analysis test.
The semen sample is collected in a sterile wide mouthed container with minimum 2-5 days of abstinence and sent to the laboratory where it is evaluated for factors like volume, concentration, motility and morphology. Absence of low sperm count does not certainly indicate that a man Is infertile, there could be an obstruction with the production or delivery of the sperm.
The semen is analysed both macroscopically and microscopically in the laboratory.
Macroscopic Examination:
Liquefaction: Semen sample must be liquefied within 30 minutes post collection.
Viscosity: Normal viscosity will leave the pipette in small discrete drops. Abnormal viscosity will leave a thread of more than 2 cm.
Appearance: Normal sample gives an appearance of grey opalascent. It may be less opaque if low sperm concentration, reddish if it contains red blood cells (Haemospermia), yellowish if a man is having jaundice or on some medications.
Volume: Ideal volume should be 1.4 ml to 1.7 ml.
pH: Ideal pH is 7.2 and should be assessed once the sample is completely liquefied.
Microscopic Examination
Semen Volume: On an average a man produces 2-5ml of semen. If the volume is low or absent then it could lead to problems like
- Inability to ejaculate
- Problems or absence of the ejaculatory duct
- Short abstinence
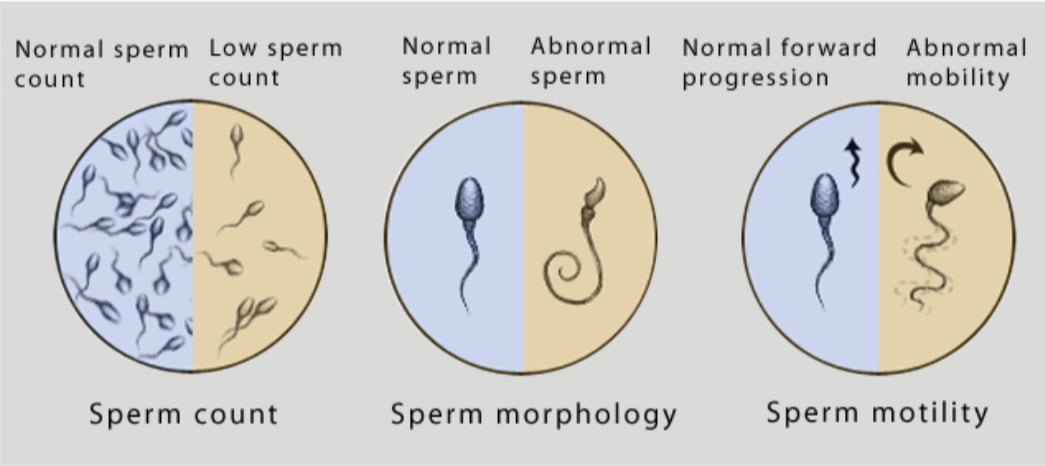
Sperm Concentration:
Sperm concentration should be minimum 15 million per ml as per the WHO latest guidelines. If the concentration is lower that the condition is called a Oligozoospermia, if no sperms are seen in the ejaculate it is called a Azoospermia ( assessed after evaluating minimum 2 sample 3-5 days apart) and if the sperm concentration is below 5 million/ml then is considered as severe Oligozoospermia.
Sperm Motility:
Healthy sperm motility is forward progression in a linear motion. Ideal motility should be 40% with 32% Progressive Motility (PR). The motility must be assessed as soon as the sample is liquefied preferably in 30 min after collection less than that is referred to as Asthenozoospermia.
Sperm Morphology:
It refers to the shape and appearance ( head, mid-piece, and tail) of the spermatozoa. 4% normal sperms in the ejaculate is considered to be normal and less than that is referred to as Teratozoospermia.
Sperm Vitality:
Sperm vitality refers to the proportion of live membrane intact speramatozoa. 58% normal intact spermatozoa in the semen is considered to be normal. It is an important factor if the motile sperms are low in number.
The laboratory at AFGC assess all the semen parameters carefully for the better diagnoses and treatment for the patient to give the best results and fulfill the dreams of parenthood.
For further queries related to the treatment, Please call +91-9871250235 or write to contact@advancefertility.in